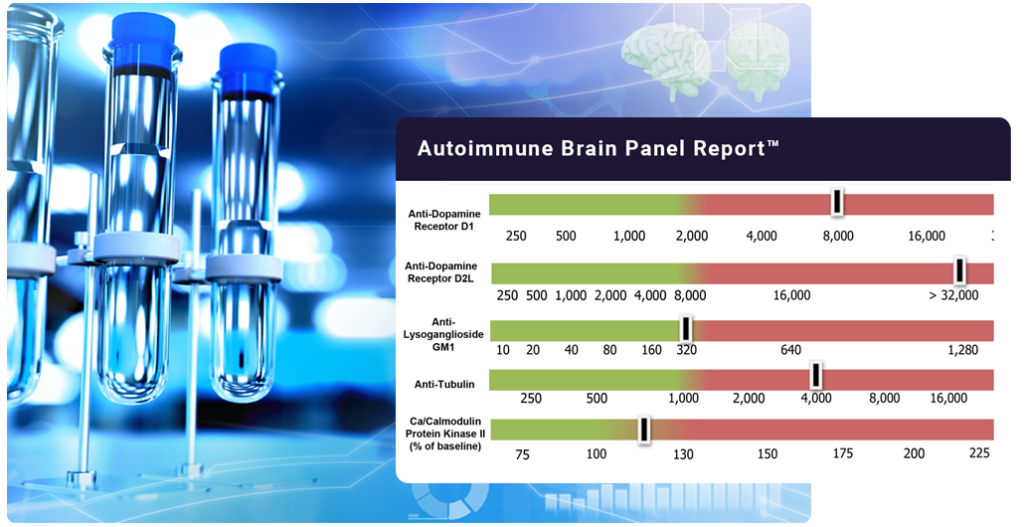
Autoimmune Brain Panel™
We look beneath the surface to bring you answers.
The Autoimmune Brain Panel™ is comprised of 5 tests which measure the levels of autoantibodies directed against specific targets in the brain and the ability of these autoantibodies to trigger neuropsychiatric symptoms.
Autoantibody Assays
Four of these tests measure the levels of autoimmune antibodies directed against specific targets in the brain including the Dopamine D1 receptor, Dopamine D2 receptor, Lysoganglioside GM1 and Tubulin.
Each of these targets is associated with certain neurologic and psychiatric symptoms. When autoantibodies are present and bind to or block these targets, it can disrupt the way the receptors and cells function, leading to the onset of neurologic and psychiatric symptoms.
Cell Stimulation Assay
The fifth test measures the stimulatory activity of the CaMKII in human brain cells, which regulates the production of certain neurotransmitters. This test measures the ability of a patient’s autoantibodies to stimulate neurologic and/or psychiatric symptoms. The CaMKII can also assist in determining the likelihood of an active infection or reinfection.
Test results you can rely on.
The Autoimmune Brain Panel™ is considered positive if one or more of the individual test results exceeds the normal range. A positive test indicates that a patient’s neurologic and/or psychiatric symptoms may be due to an autoimmune dysfunction, rather than a classic neurologic or psychiatric disorder.
Findings from our patient population study suggest that testing with the Autoimmune Brain Panel™ may be beneficial in helping to diagnose and treat patients with immune-mediated neuropsychiatric disorders. 1
Symptoms associated with targets comprising the Panel
Our patient population analysis found the following symptoms tend to correlate with specific assays. 1
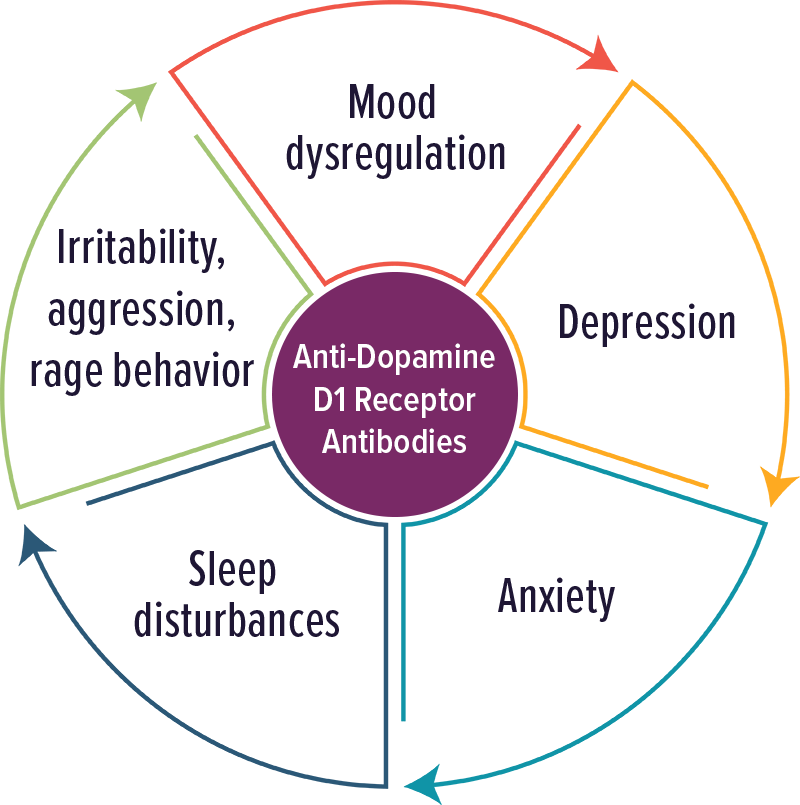
Dopamine D1 Receptor Antibodies
Individuals with elevated levels of autoantibodies against Dopamine D1 receptor typically experienced psychiatric symptoms, including psychosis. Other symptoms included: mood dysregulation, anxiety, depression, sleep disturbances, irritability, aggression and rage behavior.
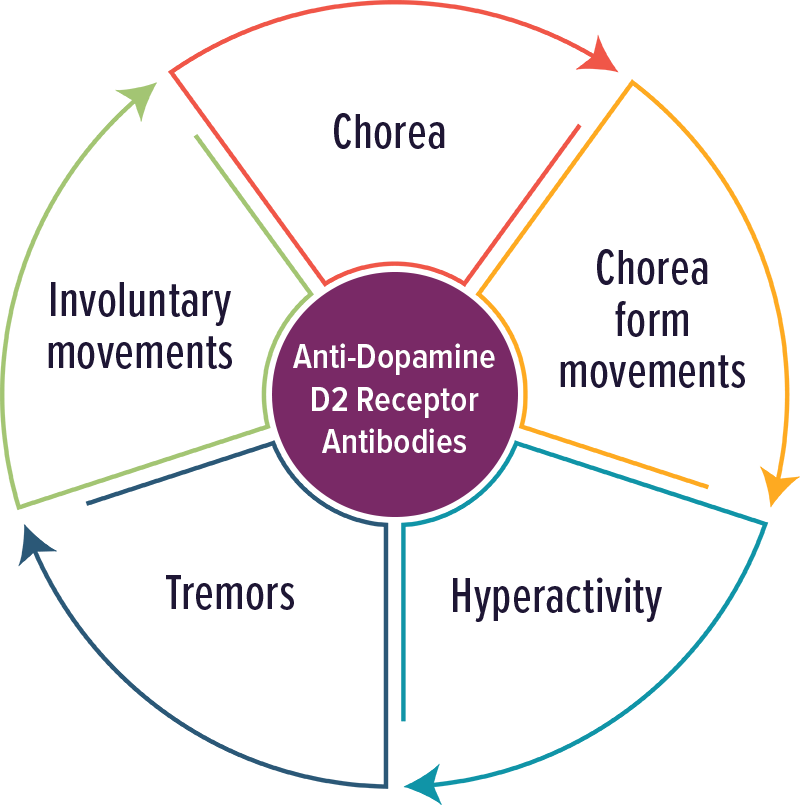
Dopamine D2 Receptor Antibodies
Individuals with elevated levels of autoantibodies against Dopamine D2 receptor typically experienced movement disorders and impulsivity. Other symptoms included: chorea, chorea form movements, hyperactivity, tremors and involuntary movements.
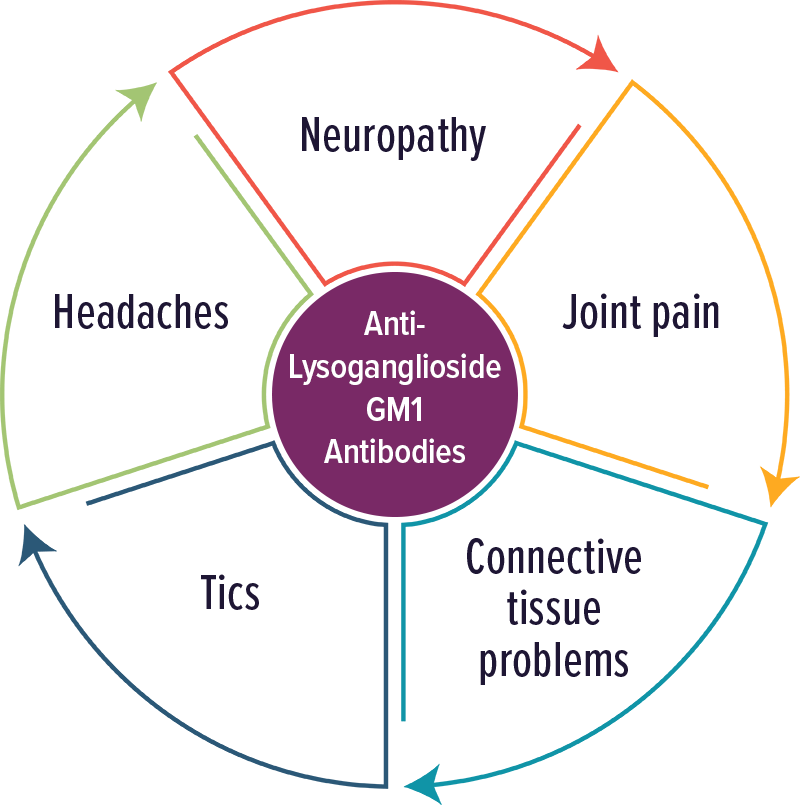
Lysoganglioside GM1 Antibodies
Individuals with elevated levels of autoantibodies against Lysoganglioside GM1 typically experienced neuropathic symptoms, including tics. Other symptoms included: neuropathy, joint pain, connective tissue problems, tics and headaches.
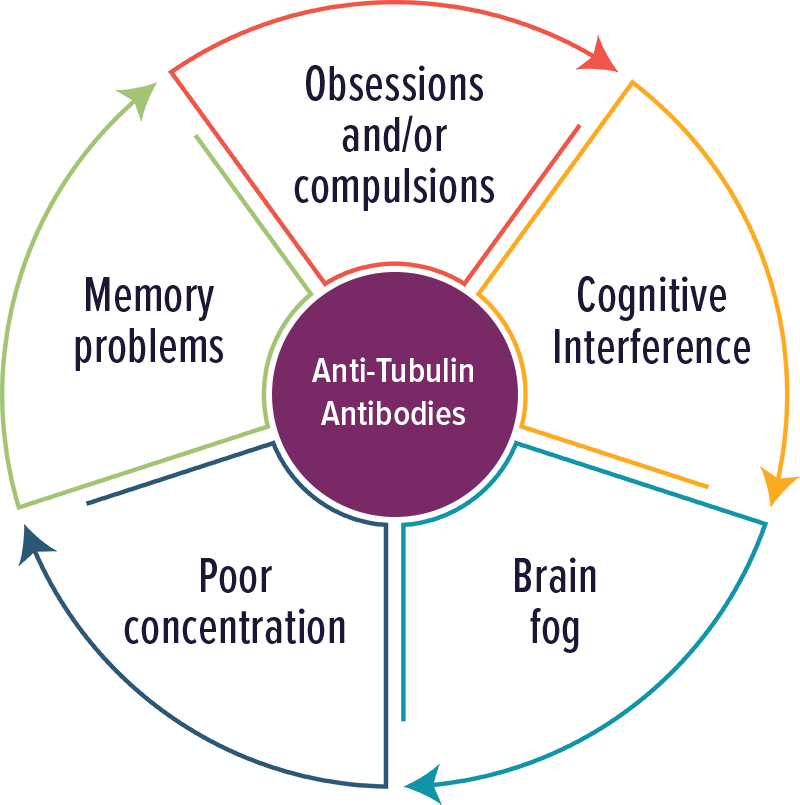
Tubulin Antibodies
Individuals with elevated levels of autoantibodies against Tubulin typically experienced cognitive complaints, OCD and brain fog. Other symptoms included: poor concentration and memory problems.
CaMKII – A Cell Stimulation Assay
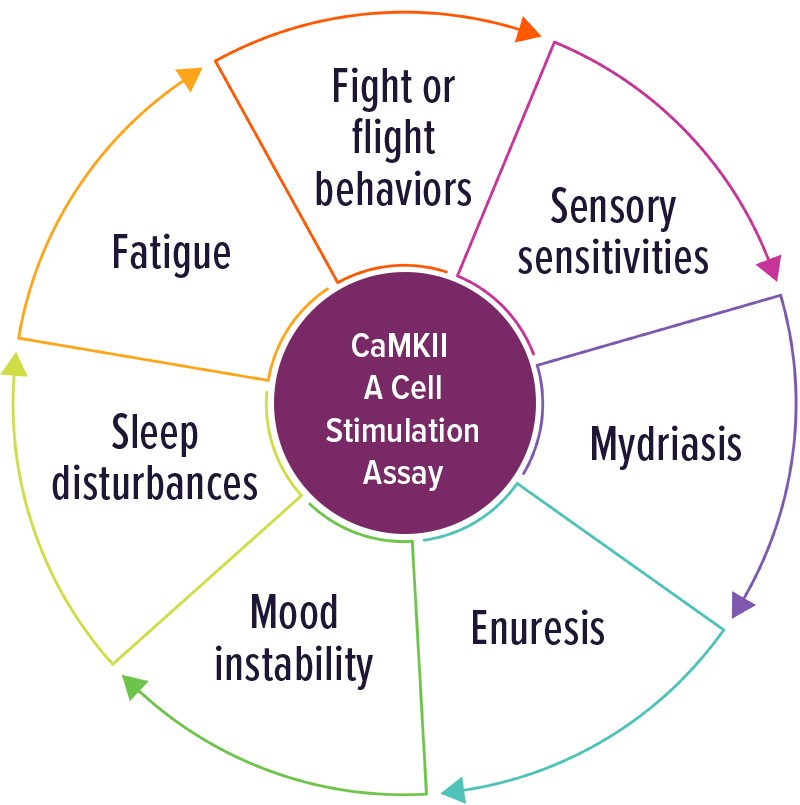
Individuals with elevated CaMKII levels were often positive with involuntary movements and any symptom of adrenergic activation. Other symptoms included: fight or flight behaviors, sensory abnormalities, fatigue, sleep disturbance, mood instability, enuresis and mydriasis.




Improving patient outcomes through precision testing.
Testing with the Autoimmune Brain Panel™ reveals that a 10-year-old child, who was initially diagnosed with a seizures disorder, actually suffers from a treatable infection-induced autoimmune condition. The young girl experienced choreiform movements, along with multiple neurologic and psychiatric symptoms. Elevated test results supported an underlying autoimmune basis for her symptoms. She had a complete resolution of symptoms following treatment with immunomodulatory therapy.
Backed by more than 2 decades of research.
References
- Shimasaki C, Frye RE, Trifiletti R, Cooperstock M, Kaplan G, Melamed I, Greenberg R, Katz A, Fier E, Kem D, Traver D, Dempsey T, Latimer ME, Cross A, Dunn JP, Bentley R, Alvarez K, Reim S, Appleman J. Evaluation of the Cunningham Panel™ in pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorder associated with streptococcal infection (PANDAS) and pediatric acute-onset neuropsychiatric syndrome (PANS): Changes in antineuronal antibody titers parallel changes in patient symptoms. J Neuroimmunol. 2020 Feb 15;339:577138. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2019.577138. Epub 2019 Dec 15. PMID: 31884258. https://www.jni-journal.com/article/S0165-5728(19)30352-2/fulltext