Autoimmune Brain Panel™ Results and Symptom Correlation
Neuropsychiatric symptoms correlate with neuronal targets
Listed below are various symptoms which tend to correlate with specific test results in our clinical laboratory patient population analysis.
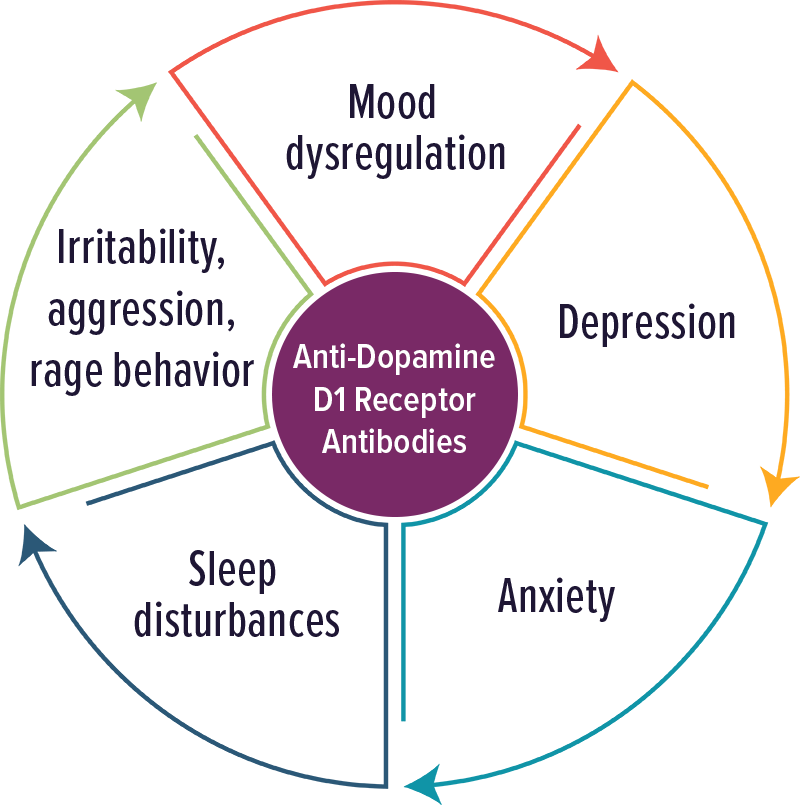
Anti-Dopamine D1 Receptor Antibodies
Individuals with elevated levels of autoantibodies against Dopamine D1 receptor typically experienced psychiatric symptoms, including psychosis.
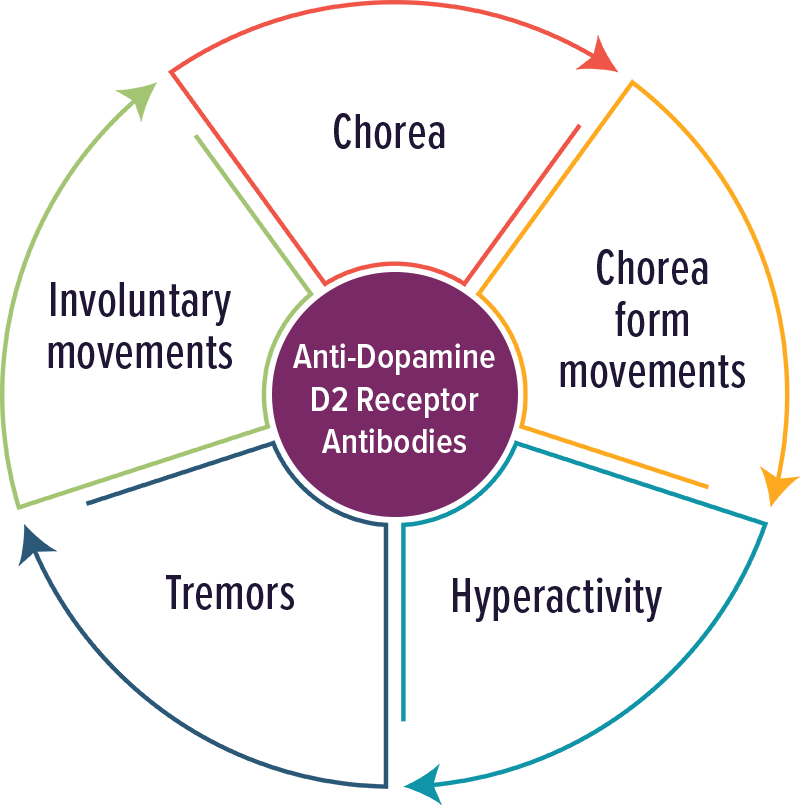
Anti-Dopamine D2 Receptor Antibodies
Individuals with elevated levels of autoantibodies against Dopamine D2 receptor typically experienced movement disorders and impulsivity.
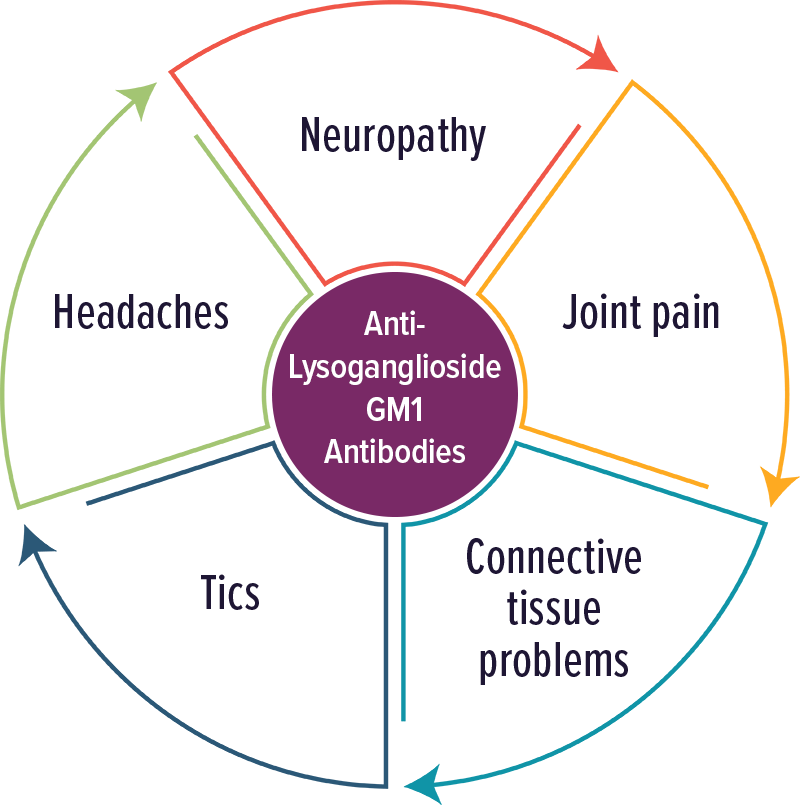
Anti-Lysoganglioside GM1 Antibodies
Individuals with elevated levels of autoantibodies against Lysoganglioside GM1 typically experienced neuropathic symptoms, including tics.
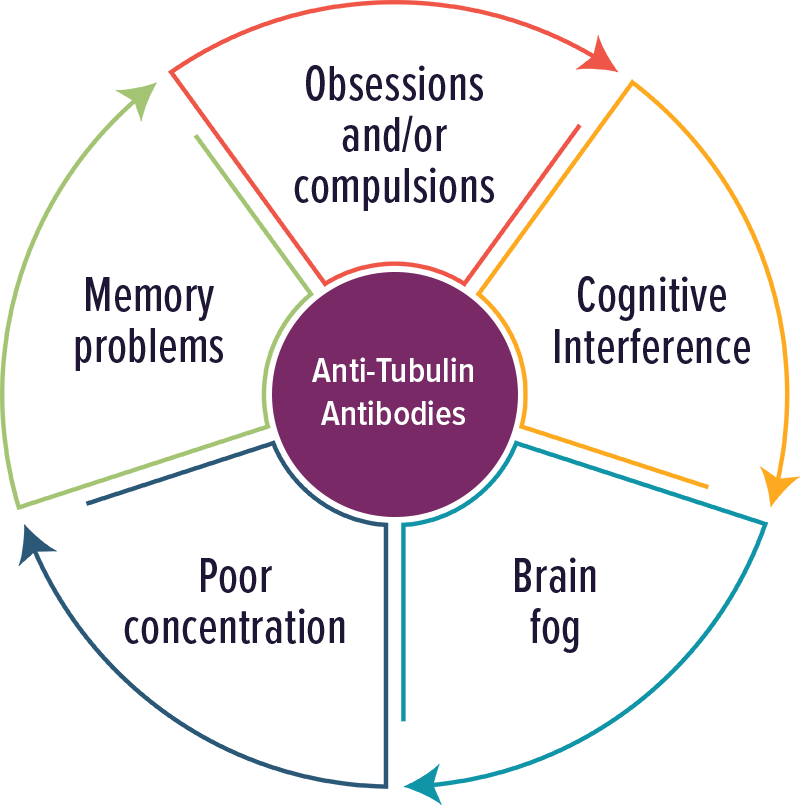
Anti-Tubulin Antibodies
Individuals with elevated levels of autoantibodies against Tubulin typically experienced cognitive complaints, OCD and brain fog.
CaMKII – A Cell Stimulation Assay
Individuals with elevated CaMKII levels were often positive with involuntary movements and any symptom of adrenergic activation.
An elevated CaMKII result indicates a patient’s autoantibodies are stimulating this enzyme. CaMKII is responsible for upregulating brain neurotransmitters such as dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine.
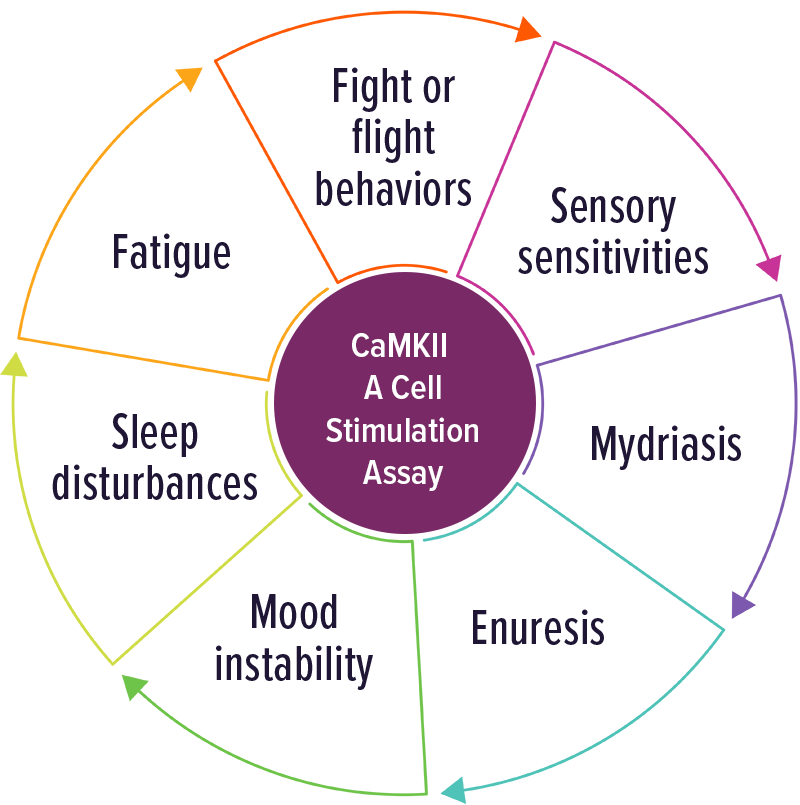
CaMKII activation may result in disrupted neuronal functioning, and trigger a variety of neurologic and/or psychiatric symptoms.